Clean Bench vs Biosafety Cabinet: What’s the Difference?

Institutional biosafety committees (IBCs) frequently receive questions about the proper type of hood for use with biological materials and the difference between biosafety cabinets versus clean benches. While both pieces of equipment are hoods with directional airflow, they function differently and are intended for different purposes. This article explores how these tools work and why biosafety cabinets are preferred in research involving cell and gene therapies.
What is a Biosafety Cabinet?
Biosafety cabinets (BSCs) protect the product as well as the user and the environment. They operate under negative air pressure (i.e., suck inward), protecting the user from exposure to aerosolized infectious agents. The air sucked into the hood is sterilized by high efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration before being exhausted out, thereby protecting the environment.
How is a Biosafety Cabinet Different from a Clean Bench?
Clean benches or laminar flow hoods work under positive air pressure (i.e., blow outward) and are only intended for work with non-hazardous materials. Use of hazardous materials in a clean bench can increase the risk of occupational exposure and contamination of the room in which the work is being done.
We’ve also created the following quick reference guide to illustrate the difference between these tools and their airflows.
Biosafety Cabinet (BSC)
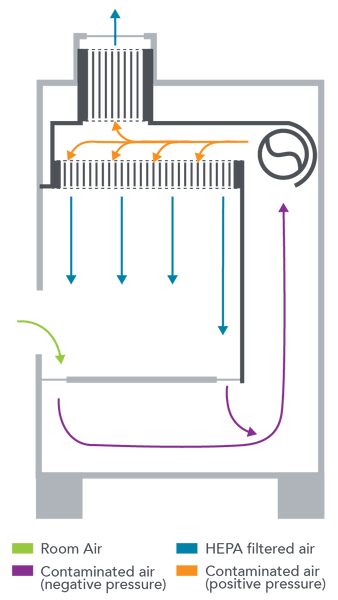
BSCs operate under negative air pressure (i.e., sucks inward), protecting the user from exposure to aerosolized infectious agents. Any infectious aerosols are sucked in through the grills positioned at the front and back of the work surface and removed by HEPA filtration. The hood also blows sterile (HEPA filtered air) from the top down towards the work surface to protect the product from contamination with non-sterile ambient room air.
Clean Bench or Laminar Flow Hood

Clean benches are only intended for work with non-hazardous materials. A clean bench operates under positive pressure and blow sterile (HEPA filtered) air towards the worker, preventing the product from being contaminated with non-sterile ambient room air. If a clean bench is utilized with infectious agents or other hazardous materials, it will blow those materials towards the worker and increase their risk of exposure. It will also spread contamination throughout the room.
Why Does the IBC Prefer Researchers use a Biosafety Cabinet vs a Clean Bench?
BSCs provide a greater measure of safety than working on a countertop. They provide sterile air to prevent environmental contamination of the investigational product and sterilize the exhaust air to prevent occupational exposure and environmental release of the drug. In the case of IBC review, we’re preventing exposure to biologics such as engineered genetic materials and/or infectious agents.
Disinfecting Work Surfaces in Clean Benches and Biosafety Cabinets
Work surfaces, such as the horizontal surface inside the BSCs, must be disinfected following work or spills involving biohazardous materials. Disinfectants registered with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) should be utilized. Also, be mindful of whether the disinfectant is compatible for use with the hood’s metal surface. Some research sites utilize 10% bleach solutions for disinfection. Bleach is corrosive and can cause metal surfaces to rust if left on the surface for extended periods. If you utilize bleach to disinfect metal surfaces, remember to remove the bleach after sufficient contact time has elapsed for disinfection (i.e., 5-10 minutes), and then remove the bleach with either water, 70% ethanol, or other disinfectant wipes to protect the metal surfaces.
Not all hoods are created equal. While a BSC provides greater protection of the investigational product, the research staff, and the environment, a clean bench can actually increase the risk of occupational exposure, contaminating the pharmacy area, and environmental release with the investigational product.



