Antibiotic resistance may spread even more easily than expected
Scienmag
JANUARY 20, 2021
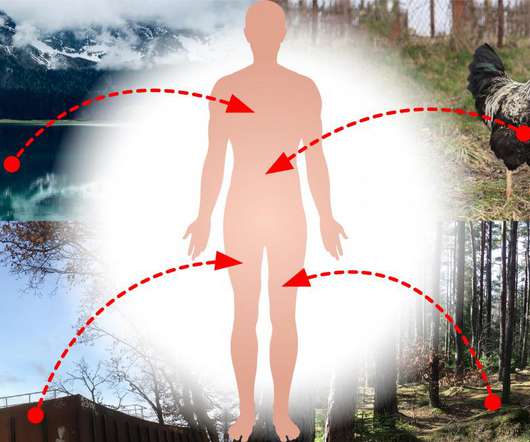
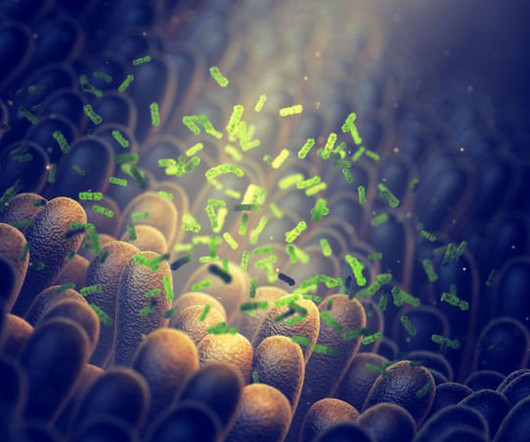
Credit: Jan Zrimec/Chalmers University of Technology Pathogenic bacteria in humans are developing resistance to antibiotics much faster than expected. Now, computational research at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, shows that one reason could be significant genetic transfer between bacteria in our ecosystems and to humans.











Let's personalize your content