New ‘atlas’ charts how antibodies attack spike protein variants
Scienmag
JULY 23, 2021
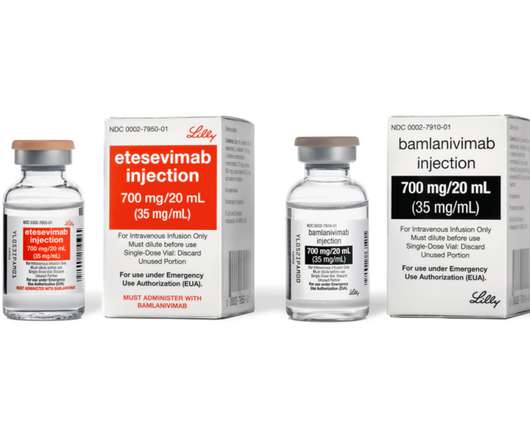
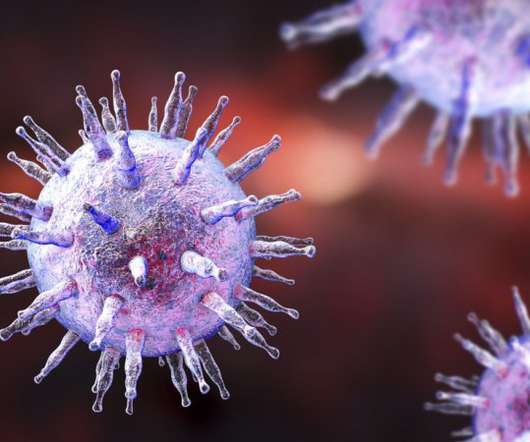
Antibodies capable of neutralizing multiple SARS-CoV-2 strains can inform strategies for broadly protective COVID-19 booster vaccines As the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 continues to evolve, immunologists and infectious diseases experts are eager to know whether new variants are resistant to the human antibodies that recognized initial versions (..)




































Let's personalize your content