Intravacc gets NIAID contract for intranasal gonorrhoea vaccine development
Pharmaceutical Technology
OCTOBER 6, 2022
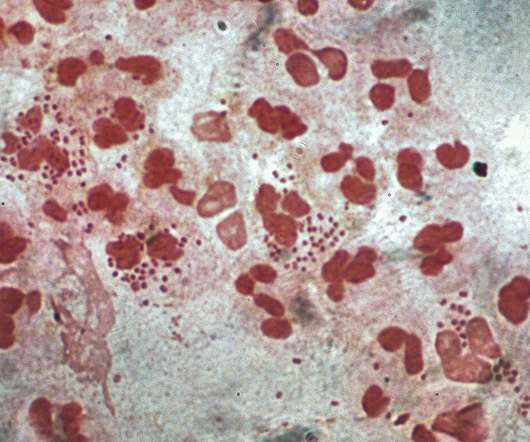
from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH) unit National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) to develop a prophylactic intranasal vaccine against Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG). Leveraging its outer membrane vesicles (OMV) platform technology, Intravacc will develop the vaccine.

































Let's personalize your content