A new dawn of the genomic age: five areas set to be transformed in 2023
pharmaphorum
JANUARY 26, 2023
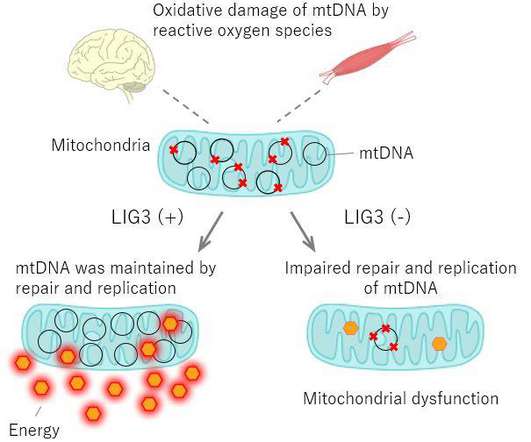
2022 was a banner year for genomics. In March, the collaborative T2T consortium published the first complete telomere-to-telomere sequence of the human genome, filling in the last 8% of the 3 billion base pairs that make up our DNA.








































Let's personalize your content